


Python培训
400-996-5531
python、区块链、人工智能等,在近一两年内炒的比较火热,对于python、人工智能,相比来说比较容易理解,但是对于什么是区块链、区块链技术的工作原理、怎样搭建属于自己的区块链可能不是很了解,今天我们就来解决你的这些疑问。
什么是区块链?
记住,区块链是一个不可变的、有序的被称为块的记录链。它们可以包含交易、文件或任何您喜欢的数据。但重要的是,他们用哈希一起被链接在一起。
本指南的目的是什么?
你可以舒服地阅读和编写基础的Python,因为我们将通过HTTP与区块链进行讨论,所以你也要了解HTTP的工作原理。
你需要准备什么?
确定安装了 Python 3.6+ (还有 pip) ,你还需要安装 Flask、 Requests 库:
pip install
Flask
==
0.12
.
2
requests
==
2.18
.
4
对了, 你还需要一个支持HTTP的客户端, 比如 Postman 或者 cURL,其他也可以。
Step 1: 创建一个区块链
打开你最喜欢的文本编辑器或者IDE, 我个人比较喜欢 PyCharm. 新建一个名为 blockchain.py的文件。 我们将只用这一个文件就可以。.
描述区块链
我们要创建一个 Blockchain 类 ,他的构造函数创建了一个初始化的空列表(要存储我们的区块链),并且另一个存储交易。下面是我们这个类的实例:
blockchain.py
class
Blockchain
(
object
):
def
__init__
(
self
):
self
.
chain
=
[]
self
.
current_transactions
=
[]
def
new_block
(
self
):
# Creates a new Block and adds it to the chain
pass
def
new_transaction
(
self
):
# Adds a new transaction to the list of transactions
pass
@staticmethod
def
hash
(
block
):
# Hashes a Block
pass
@property
def
last_block
(
self
):
# Returns the last Block in the chain
pass
我们的 Blockchain 类负责管理链式数据,它会存储交易并且还有添加新的区块到链式数据的Method。让我们开始扩充更多Method。
块是什么样的 ?
每个块都有一个 索引,一个 时间戳(Unix时间戳),一个 事务列表, 一个 校验(稍后详述) 和 前一个块的散列 。
下面是一个Block的例子 :
blockchain.py
block
=
{
'index'
:
1
,
'timestamp'
:
1506057125.900785
,
'transactions'
:
[
{
'sender'
:
"8527147fe1f5426f9dd545de4b27ee00"
,
'recipient'
:
"a77f5cdfa2934df3954a5c7c7da5df1f"
,
'amount'
:
5
,
}
],
'proof'
:
324984774000
,
'previous_hash'
:
"2cf24dba5fb0a30e26e83b2ac5b9e29e1b161e5c1fa7425e73043362938b9824"
}
在这一点上,一个区块链的概念应该是明显的-每个新块都包含在其内的前一个块的散列 。 这是至关重要的,因为这是区块链不可改变的原因:如果攻击者损坏 区块链 中较早的块,则所有后续块将包含不正确的哈希值。
这有道理吗? 如果你还没有想通,花点时间仔细思考一下——这是区块链背后的核心理念。
添加交易到区块
我们将需要一个添加交易到区块的方式。我们的 new_transaction()方法的责任就是这个, 并且它非常的简单:
blockchain.py
class
Blockchain
(
object
):
...
def
new_transaction
(
self
,
sender
,
recipient
,
amount
):
"""
Creates a new transaction to go into the next mined Block
:param sender: <str> Address of the Sender
:param recipient: <str> Address of the Recipient
:param amount: <int> Amount
:return: <int> The index of the Block that will hold this transaction
"""
self
.
current_transactions
.
append
({
'sender'
:
sender
,
'recipient'
:
recipient
,
'amount'
:
amount
,
})
return
self
.
last_block
[
'index'
]
+
1
new_transaction() 方法添加了交易到列表,它返回了交易将被添加到的区块的索引---讲开采下一个这对稍后对提交交易的用户有用。
创建新的区块
当我们的 Blockchain 被实例化后,我们需要将 创世 区块(一个没有前导区块的区块)添加进去进去。我们还需要向我们的起源块添加一个 证明,这是挖矿的结果(或工作证明)。 我们稍后会详细讨论挖矿。
除了在构造函数中创建 创世 区块外,我们还会补全 new_block() 、 new_transaction() 和 hash() 函数:
blockchain.py
import
hashlib
import
json
from
time
import
time
class
Blockchain
(
object
):
def
__init__
(
self
):
self
.
current_transactions
=
[]
self
.
chain
=
[]
# 创建创世区块
self
.
new_block
(
previous_hash
=
1
,
proof
=
100
)
def
new_block
(
self
,
proof
,
previous_hash
=
None
):
"""
创建一个新的区块到区块链中
:param proof: <int> 由工作证明算法生成的证明
:param previous_hash: (Optional) <str> 前一个区块的 hash 值
:return: <dict> 新区块
"""
block
=
{
'index'
:
len
(
self
.
chain
)
+
1
,
'timestamp'
:
time
(),
'transactions'
:
self
.
current_transactions
,
'proof'
:
proof
,
'previous_hash'
:
previous_hash
or
self
.
hash
(
self
.
chain
[-
1
]),
}
# 重置当前交易记录
self
.
current_transactions
=
[]
self
.
chain
.
append
(
block
)
return
block
def
new_transaction
(
self
,
sender
,
recipient
,
amount
):
"""
创建一笔新的交易到下一个被挖掘的区块中
:param sender: <str> 发送人的地址
:param recipient: <str> 接收人的地址
:param amount: <int> 金额
:return: <int> 持有本次交易的区块索引
"""
self
.
current_transactions
.
append
({
'sender'
:
sender
,
'recipient'
:
recipient
,
'amount'
:
amount
,
})
return
self
.
last_block
[
'index'
]
+
1
@property
def
last_block
(
self
):
return
self
.
chain
[-
1
]
@staticmethod
def
hash
(
block
):
"""
给一个区块生成 SHA-256 值
:param block: <dict> Block
:return: <str>
"""
# 我们必须确保这个字典(区块)是经过排序的,否则我们将会得到不一致的散列
block_string
=
json
.
dumps
(
block
,
sort_keys
=
True
).
encode
()
return
hashlib
.
sha256
(
block_string
).
hexdigest
()
上面的代码应该是直白的 --- 为了让代码清晰,我添加了一些注释和文档说明。 我们差不多完成了我们的区块链。 但在这个时候你一定很疑惑新的块是怎么被创建、锻造或挖掘的。
工作量证明算法
使用工作量证明(PoW)算法,来证明是如何在区块链上创建或挖掘新的区块。PoW 的目标是计算出一个符合特定条件的数字,这个数字对于所有人而言必须在计算上非常困难,但易于验证。这是工作证明背后的核心思想。
我们将看到一个简单的例子帮助你理解:
假设一个整数 x 乘以另一个整数 y 的积的 Hash 值必须以 0 结尾,即 hash(x * y) = ac23dc...0。设 x = 5,求 y ?用 Python 实现:
from
hashlib
import
sha256
x
=
5
y
=
0
# We don't know what y should be yet...
while
sha256
(
f
'{x*y}'
.
encode
()).
hexdigest
()[-
1
]
!=
"0"
:
y
+=
1
(
f
'The solution is y = {y}'
)
结果是: y = 21。因为,生成的 Hash 值结尾必须为 0。
hash
(
5
*
21
)
=
1253e9373e
...
5e3600155e860
在比特币中,工作量证明算法被称为 Hashcash ,它和上面的问题很相似,只不过计算难度非常大。这就是矿工们为了争夺创建区块的权利而争相计算的问题。 通常,计算难度与目标字符串需要满足的特定字符的数量成正比,矿工算出结果后,就会获得一定数量的比特币奖励(通过交易)。
验证结果,当然非常容易。
实现工作量证明
让我们来实现一个相似 PoW 算法。规则类似上面的例子:
找到一个数字 P ,使得它与前一个区块的 proof 拼接成的字符串的 Hash 值以 4 个零开头。
blockchain.py
import
hashlib
import
json
from
time
import
time
from
uuid
import
uuid4
class
Blockchain
(
object
):
...
def
proof_of_work
(
self
,
last_proof
):
"""
Simple Proof of Work Algorithm:
- Find a number p' such that hash(pp') contains leading 4 zeroes, where p is the previous p'
- p is the previous proof, and p' is the new proof
:param last_proof: <int>
:return: <int>
"""
proof
=
0
while
self
.
valid_proof
(
last_proof
,
proof
)
is
False
:
proof
+=
1
return
proof
@staticmethod
def
valid_proof
(
last_proof
,
proof
):
"""
Validates the Proof: Does hash(last_proof, proof) contain 4 leading zeroes?
:param last_proof: <int> Previous Proof
:param proof: <int> Current Proof
:return: <bool> True if correct, False if not.
"""
guess
=
f
'{last_proof}{proof}'
.
encode
()
guess_hash
=
hashlib
.
sha256
(
guess
).
hexdigest
()
return
guess_hash
[:
4
]
==
"0000"
衡量算法复杂度的办法是修改零开头的个数。使用 4 个来用于演示,你会发现多一个零都会大大增加计算出结果所需的时间。
现在 Blockchain 类基本已经完成了,接下来使用 HTTP requests 来进行交互。
Step 2: Blockchain 作为 API 接口
我们将使用 Python Flask 框架,这是一个轻量 Web 应用框架,它方便将网络请求映射到 Python 函数,现在我们来让 Blockchain 运行在基于 Flask web 上。
我们将创建三个接口:
/transactions/new 创建一个交易并添加到区块
/mine 告诉服务器去挖掘新的区块
/chain 返回整个区块链
创建节点
我们的“Flask 服务器”将扮演区块链网络中的一个节点。我们先添加一些框架代码:
blockchain.py
import
hashlib
import
json
from
textwrap
import
dedent
from
time
import
time
from
uuid
import
uuid4
from
flask
import
Flask
class
Blockchain
(
object
):
...
# Instantiate our Node
app
=
Flask
(
__name__
)
# Generate a globally unique address for this node
node_identifier
=
str
(
uuid4
()).
replace
(
'-'
,
''
)
# Instantiate the Blockchain
blockchain
=
Blockchain
()
@app
.
route
(
'/mine'
,
methods
=[
'GET'
])
def
mine
():
return
"We'll mine a new Block"
@app
.
route
(
'/transactions/new'
,
methods
=[
'POST'
])
def
new_transaction
():
return
"We'll add a new transaction"
@app
.
route
(
'/chain'
,
methods
=[
'GET'
])
def
full_chain
():
response
=
{
'chain'
:
blockchain
.
chain
,
'length'
:
len
(
blockchain
.
chain
),
}
return
jsonify
(
response
),
200
if
__name__
==
'__main__'
:
app
.
run
(
host
=
'0.0.0.0'
,
port
=
5000
)
简单的说明一下以上代码:
第 15 行:实例化节点。阅读更多关于 Flask 内容。
第 18 行:为节点创建一个随机的名称。.
第 21 行:实例化 Blockchain 类。
第 24--26 行:创建 /mine 接口,GET 方式请求。
第 28--30 行:创建 /transactions/new 接口,POST 方式请求,可以给接口发送交易数据。
第 32--38 行:创建 /chain 接口,返回整个区块链。
第 40--41 行:服务器运行端口 5000 。
发送交易
发送到节点的交易数据结构如下:
{
"sender"
:
"my address"
,
"recipient"
:
"someone else's address"
,
"amount"
:
5
}
因为我们已经有了添加交易的方法,所以基于接口来添加交易就很简单了。让我们为添加事务写函数:
blockchain.py
import
hashlib
import
json
from
textwrap
import
dedent
from
time
import
time
from
uuid
import
uuid4
from
flask
import
Flask
,
jsonify
,
request
...
@app
.
route
(
'/transactions/new'
,
methods
=[
'POST'
])
def
new_transaction
():
values
=
request
.
get_json
()
# Check that the required fields are in the POST'ed data
required
=
[
'sender'
,
'recipient'
,
'amount'
]
if
not
all
(
k
in
values
for
k
in
required
):
return
'Missing values'
,
400
# Create a new Transaction
index
=
blockchain
.
new_transaction
(
values
[
'sender'
],
values
[
'recipient'
],
values
[
'amount'
])
response
=
{
'message'
:
f
'Transaction will be added to Block {index}'
}
return
jsonify
(
response
),
201
挖矿
挖矿正是神奇所在,它很简单,做了一下三件事:
1)计算工作量证明 PoW
2)——通过新增一个交易授予矿工(自己)一个币
3)构造新区块并将其添加到链中
blockchain.py
import
hashlib
import
json
from
time
import
time
from
uuid
import
uuid4
from
flask
import
Flask
,
jsonify
,
request
...
@app
.
route
(
'/mine'
,
methods
=[
'GET'
])
def
mine
():
# We run the proof of work algorithm to get the next proof...
last_block
=
blockchain
.
last_block
last_proof
=
last_block
[
'proof'
]
proof
=
blockchain
.
proof_of_work
(
last_proof
)
# We must receive a reward for finding the proof.
# The sender is "0" to signify that this node has mined a new coin.
blockchain
.
new_transaction
(
sender
=
"0"
,
recipient
=
node_identifier
,
amount
=
1
,
)
# Forge the new Block by adding it to the chain
previous_hash
=
blockchain
.
hash
(
last_block
)
block
=
blockchain
.
new_block
(
proof
,
previous_hash
)
response
=
{
'message'
:
"New Block Forged"
,
'index'
:
block
[
'index'
],
'transactions'
:
block
[
'transactions'
],
'proof'
:
block
[
'proof'
],
'previous_hash'
:
block
[
'previous_hash'
],
}
return
jsonify
(
response
),
200
注意交易的接收者是我们自己的服务器节点,我们做的大部分工作都只是围绕 Blockchain 类方法进行交互。到此,我们的区块链就算完成了,我们来实际运行下.
Step 3: 运行区块链
你可以使用 cURL 或 Postman 去和 API 进行交互。
启动 Server:
$ python blockchain
.
py
*
Running
on http
:
//127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
让我们通过请求 http://localhost:5000/mine ( GET )来进行挖矿:
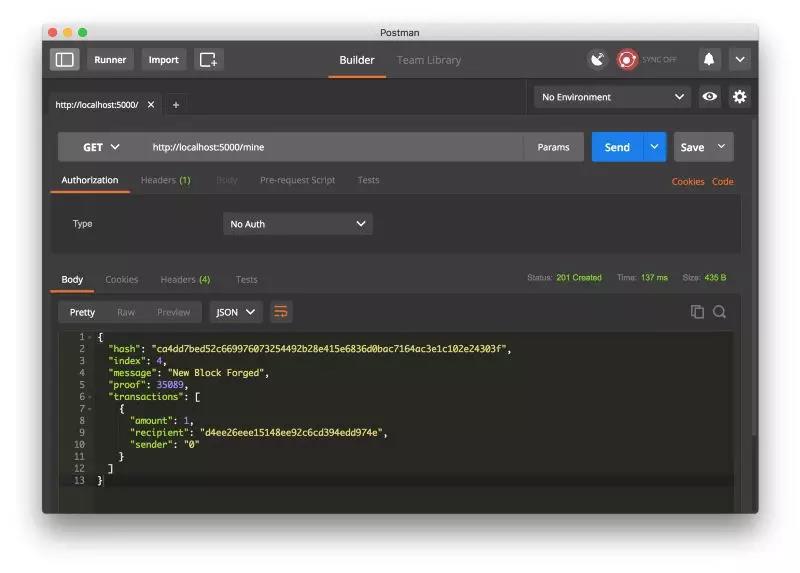
用 Postman 发起一个 GET 请求。
创建一个交易请求,请求 http://localhost:5000/transactions/new (POST),如图
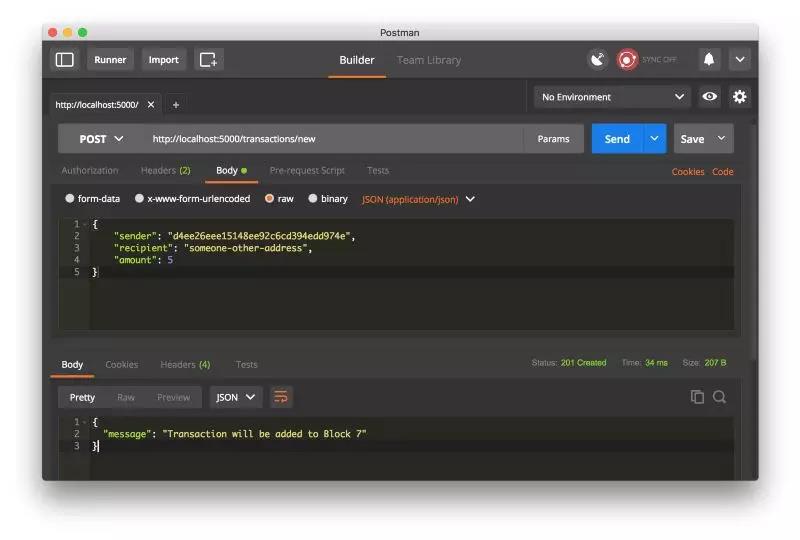
如果不是使用 Postman,则用一下的 cURL 语句也是一样的:
$ curl
-
X POST
-
H
"Content-Type: application/json"
-
d
'{
"sender": "d4ee26eee15148ee92c6cd394edd974e",
"recipient": "someone-other-address",
"amount": 5
}'
"http://localhost:5000/transactions/new"
在挖了两次矿之后,就有 3 个块了,通过请求 http://localhost:5000/chain 可以得到所有的块信息:
{
"chain"
:
[
{
"index"
:
1
,
"previous_hash"
:
1
,
"proof"
:
100
,
"timestamp"
:
1506280650.770839
,
"transactions"
:
[]
},
{
"index"
:
2
,
"previous_hash"
:
"c099bc...bfb7"
,
"proof"
:
35293
,
"timestamp"
:
1506280664.717925
,
"transactions"
:
[
{
"amount"
:
1
,
"recipient"
:
"8bbcb347e0634905b0cac7955bae152b"
,
"sender"
:
"0"
}
]
},
{
"index"
:
3
,
"previous_hash"
:
"eff91a...10f2"
,
"proof"
:
35089
,
"timestamp"
:
1506280666.1086972
,
"transactions"
:
[
{
"amount"
:
1
,
"recipient"
:
"8bbcb347e0634905b0cac7955bae152b"
,
"sender"
:
"0"
}
]
}
],
"length"
:
3
}
Step 4: 一致性(共识)
我们已经有了一个基本的区块链可以接受交易和挖矿。但是区块链系统应该是分布式的。既然是分布式的,那么我们究竟拿什么保证所有节点有同样的链呢?这就是一致性问题,我们要想在网络上有多个节点,就必须实现一个一致性的算法。
注册节点
在实现一致性算法之前,我们需要找到一种方式让一个节点知道它相邻的节点。每个节点都需要保存一份包含网络中其它节点的记录。因此让我们新增几个接口:
/nodes/register 接收 URL 形式的新节点列表。
/nodes/resolve 执行一致性算法,解决任何冲突,确保节点拥有正确的链。
我们修改下 Blockchain 的 init 函数并提供一个注册节点方法:
blockchain.py
...
from
urllib
.
parse
import
urlparse
...
class
Blockchain
(
object
):
def
__init__
(
self
):
...
self
.
nodes
=
set
()
...
def
register_node
(
self
,
address
):
"""
Add a new node to the list of nodes
:param address: <str> Address of node. Eg. 'http://192.168.0.5:5000'
:return: None
"""
parsed_url
=
urlparse
(
address
)
self
.
nodes
.
add
(
parsed_url
.
netloc
)
我们用 set 来储存节点,这是一种避免重复添加节点的简单方法.
实现共识算法
就像先前讲的那样,当一个节点与另一个节点有不同的链时,就会产生冲突。 为了解决这个问题,我们将制定最长的有效链条是最权威的规则。换句话说就是:在这个网络里最长的链就是最权威的。 我们将使用这个算法,在网络中的节点之间达成共识。
blockchain.py
...
import
requests
class
Blockchain
(
object
)
...
def
valid_chain
(
self
,
chain
):
"""
Determine if a given blockchain is valid
:param chain: <list> A blockchain
:return: <bool> True if valid, False if not
"""
last_block
=
chain
[
0
]
current_index
=
1
while
current_index
<
len
(
chain
):
block
=
chain
[
current_index
]
(
f
'{last_block}'
)
(
f
'{block}'
)
(
"-----------"
)
# Check that the hash of the block is correct
if
block
[
'previous_hash'
]
!=
self
.
hash
(
last_block
):
return
False
# Check that the Proof of Work is correct
if
not
self
.
valid_proof
(
last_block
[
'proof'
],
block
[
'proof'
]):
return
False
last_block
=
block
current_index
+=
1
return
True
def
resolve_conflicts
(
self
):
"""
This is our Consensus Algorithm, it resolves conflicts
by replacing our chain with the longest one in the network.
:return: <bool> True if our chain was replaced, False if not
"""
neighbours
=
self
.
nodes
new_chain
=
None
# We're only looking for chains longer than ours
max_length
=
len
(
self
.
chain
)
# Grab and verify the chains from all the nodes in our network
for
node
in
neighbours
:
response
=
requests
.
get
(
f
'http://{node}/chain'
)
if
response
.
status_code
==
200
:
length
=
response
.
json
()[
'length'
]
chain
=
response
.
json
()[
'chain'
]
# Check if the length is longer and the chain is valid
if
length
>
max_length
and
self
.
valid_chain
(
chain
):
max_length
=
length
new_chain
=
chain
# Replace our chain if we discovered a new, valid chain longer than ours
if
new_chain
:
self
.
chain
=
new_chain
return
True
return
False
第一个方法 valid_chain() 负责检查一个链是否有效,方法是遍历每个块并验证散列和证明。
resolve_conflicts() 是一个遍历我们所有邻居节点的方法,下载它们的链并使用上面的方法验证它们。 如果找到一个长度大于我们的有效链条,我们就取代我们的链条。
我们将两个端点注册到我们的API中,一个用于添加相邻节点,另一个用于解决冲突:
blockchain.py
@app
.
route
(
'/nodes/register'
,
methods
=[
'POST'
])
def
register_nodes
():
values
=
request
.
get_json
()
nodes
=
values
.
get
(
'nodes'
)
if
nodes
is
None
:
return
"Error: Please supply a valid list of nodes"
,
400
for
node
in
nodes
:
blockchain
.
register_node
(
node
)
response
=
{
'message'
:
'New nodes have been added'
,
'total_nodes'
:
list
(
blockchain
.
nodes
),
}
return
jsonify
(
response
),
201
@app
.
route
(
'/nodes/resolve'
,
methods
=[
'GET'
])
def
consensus
():
replaced
=
blockchain
.
resolve_conflicts
()
if
replaced
:
response
=
{
'message'
:
'Our chain was replaced'
,
'new_chain'
:
blockchain
.
chain
}
else
:
response
=
{
'message'
:
'Our chain is authoritative'
,
'chain'
:
blockchain
.
chain
}
return
jsonify
(
response
),
200
在这一点上,如果你喜欢,你可以使用一台不同的机器,并在你的网络上启动不同的节点。 或者使用同一台机器上的不同端口启动进程。 我在我的机器上,不同的端口上创建了另一个节点,并将其注册到当前节点。 因此,我有两个节点: http://localhost:5000 和 http://localhost:5001。 注册一个新节点:
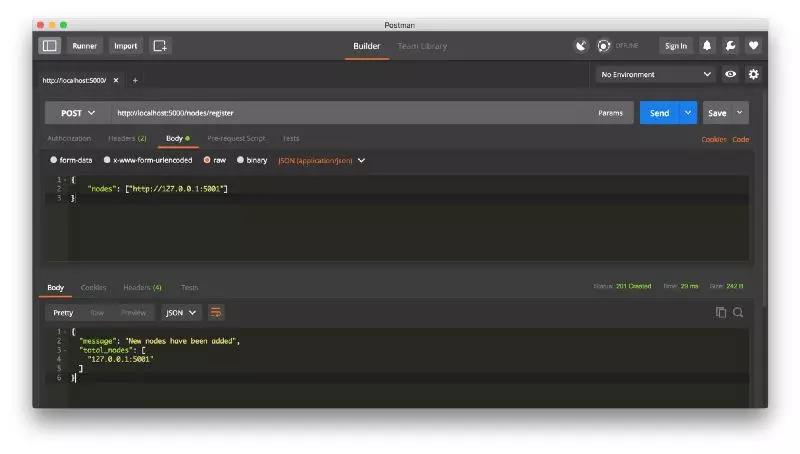
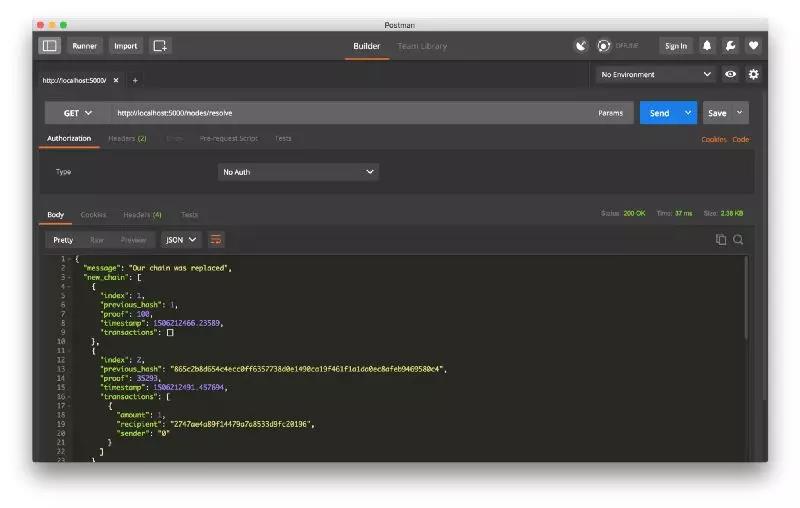
然后我在节点 2 上挖掘了一些新的块,以确保链条更长。 之后,我在节点1上调用 GET/nodes/resolve,其中链由一致性算法取代:
这是一个包,去找一些朋友一起,以帮助测试你的区块链。
恭喜你阅读完了本文,相信你已经知道了什么是区块链、也知道了区块链的工作原理是什么、并且python搭建了属于自己的区块链,同样的希望在我的抛砖引玉下,可以激励你创造更多新的东西,也许未来的某一天,区块链技术将改变我们看待事物的方式,如果你还有更多关于区块链的问题或者你想通过python培训进入到区块链这一领域,欢迎你来达内python培训班-机构进行咨询。
免责声明:内容和图片源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。
填写下面表单即可预约申请免费试听! 怕学不会?助教全程陪读,随时解惑!担心就业?一地学习,可全国推荐就业!
Copyright © Tedu.cn All Rights Reserved 京ICP备08000853号-56  京公网安备 11010802029508号 达内时代科技集团有限公司 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802029508号 达内时代科技集团有限公司 版权所有